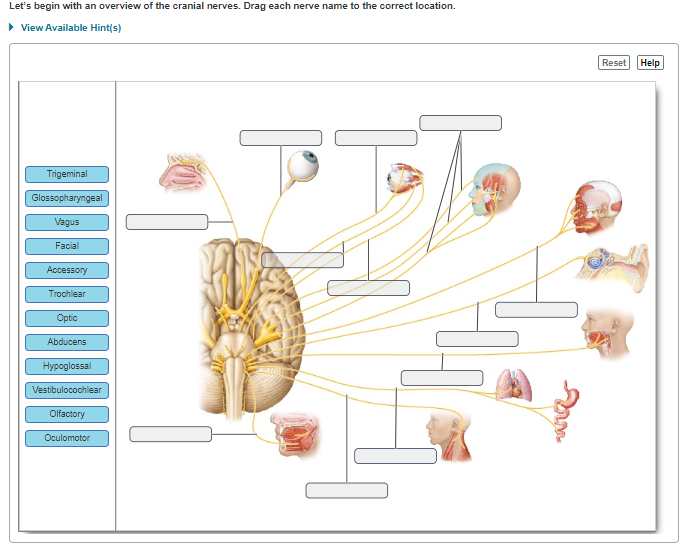
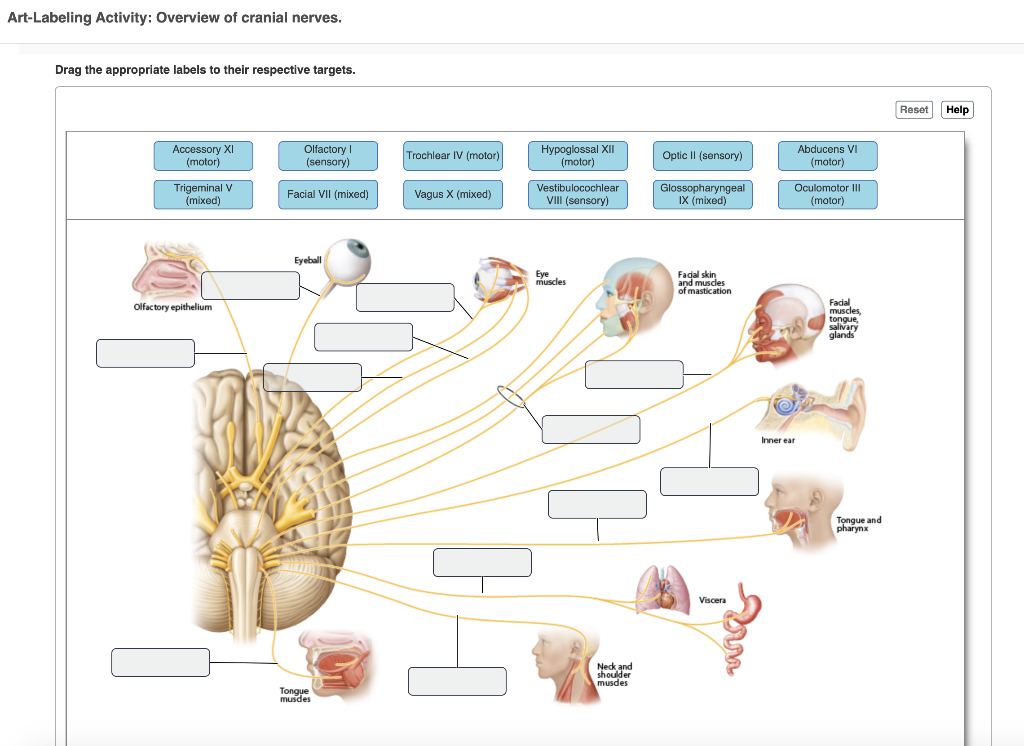
Lets Begin With An Overview Of The Cranial Nerves Drag Each Nerve Name To The Correct Location
Anatomy Exam 2 Flashcards Easy Notecards

14 5 Sensory And Motor Pathways Anatomy Physiology
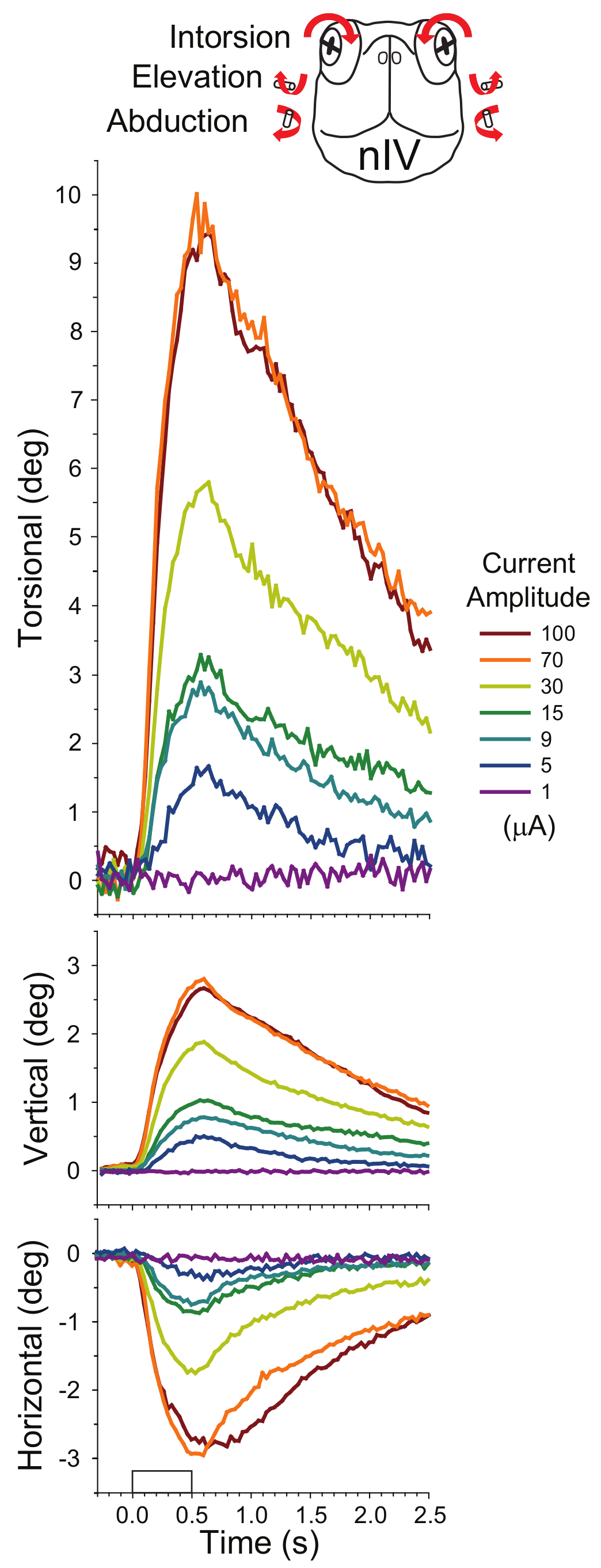
Ocular Kinematics Measured By In Vitro Stimulation Of The Cranial Nerves In The Turtle Abstract Europe Pmc

Openstax Anatomy And Physiology Ch14 The Somatic Nervous System Top Hat
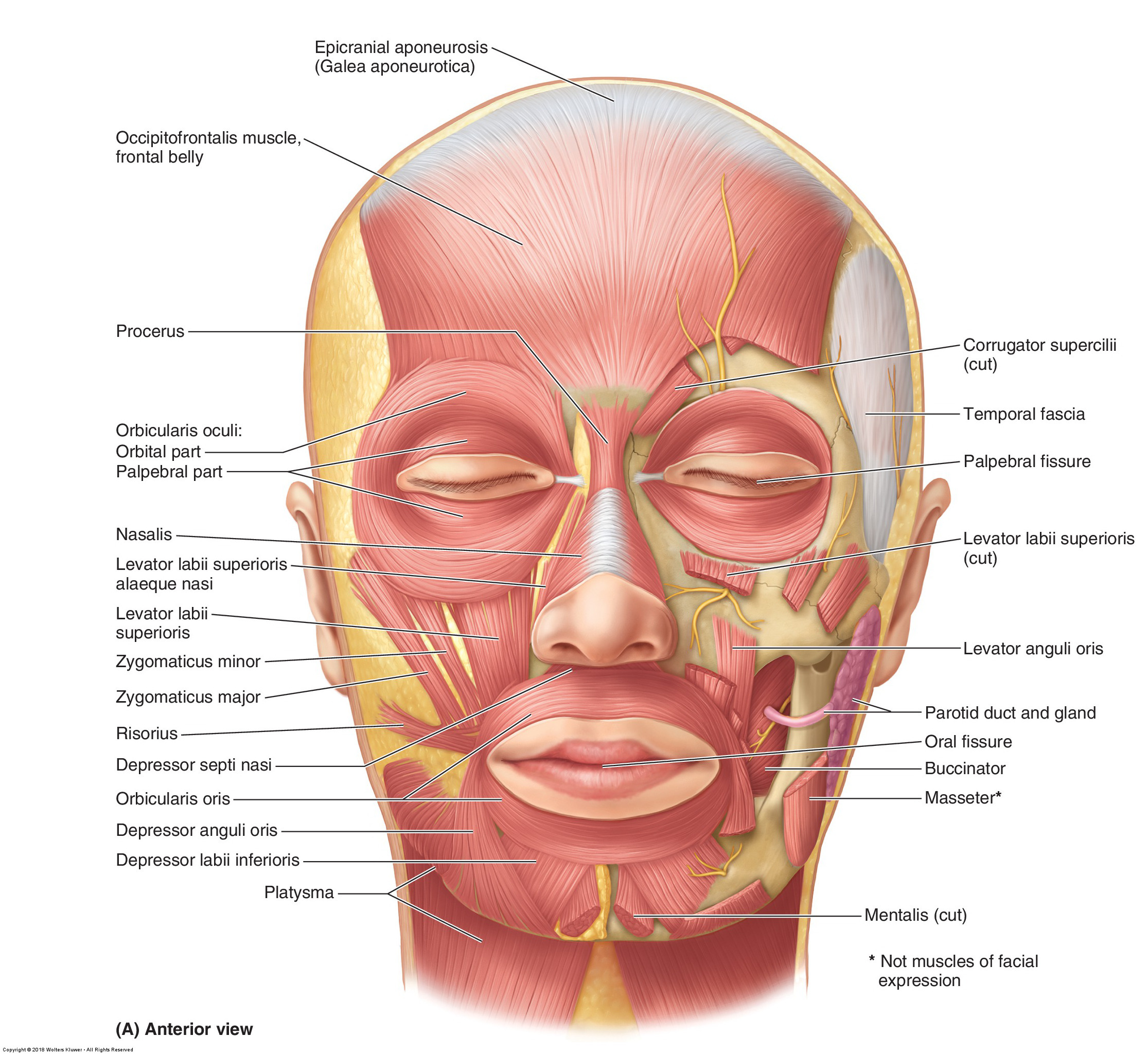
Neuroanatomy
Anatomy Exam 2 Flashcards Easy Notecards
WHICH OF THE FOLLOWING CRANIAL NERVES BEGIN OF END IN THE PONS?.

Lets begin with an overview of the cranial nerves drag each nerve name to the correct location. Increases the mobility of the digestive tract. And pupillary constriction 4. Except for the first two cranial nerves, which are considered direct extensions of the brain itself, all cranial nerves emanate from the brainstem.
Your cranial nerves are pairs of nerves that connect your brain to different parts of your head, neck, and trunk. A shoutout is a way to let people know of a game. Cranial nerves are those nerves which arise from the brain and brain stem rather than the spinal cord.
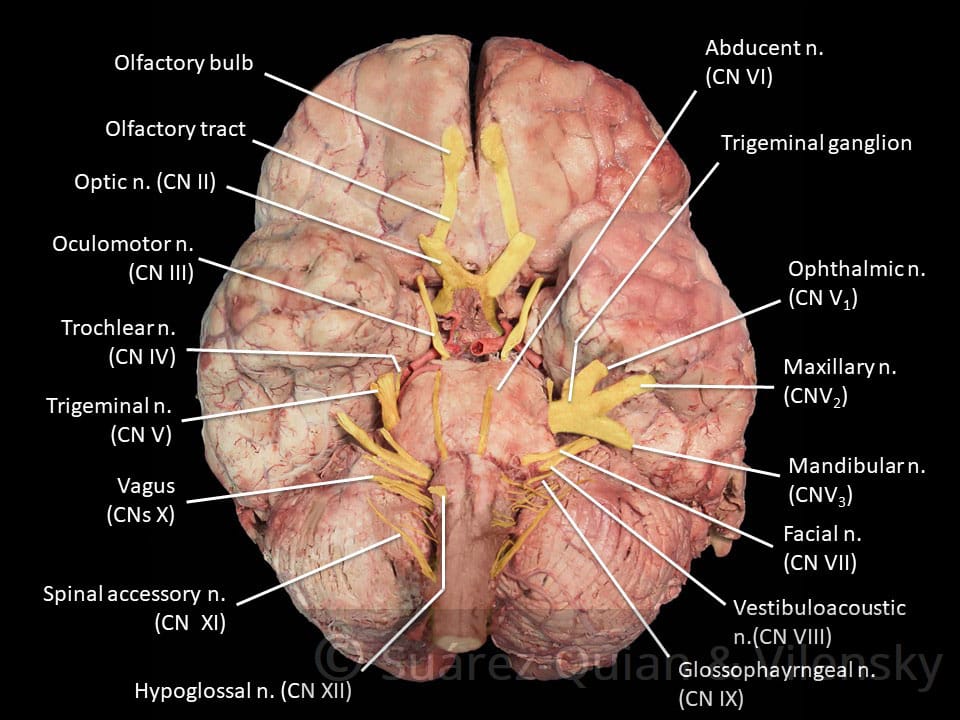
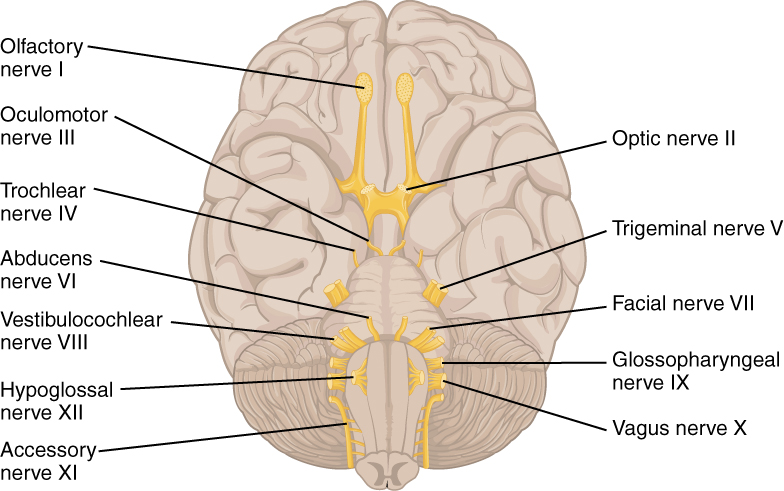
Viewing the Cranial Nerves Twelve pairs of cranial nerves emerge from the underside of the brain, pass through openings in the skull, and lead to parts of the head, neck, and trunk. Individual peripheral nerve fibers are classified based on the diameter, signal conduction velocity, and myelination state of the axons, as well as by the type of information transmitted and the organs they innervate. The cranial nerves listed here are I Olfactory, II Optic, III Oculomotor, IV Trochlear, V Trigeminal, VI Abducens, VII Facial, VIII Vestibulocochlear, IX Glossopharyngeal, X Vagus, XI Accessory, and XII Hypoglossal.
Cranial nerves III and IV arise from the midbrain, V-VIII from the pons and the lower cranial nerves IX-XII from the medulla. The cranial nerve functions are broken up into managing different aspects of your body’s daily tasks from chewing and biting to motor function, hearing, sense of smell, and vision. Other cranial nerves control muscles;.
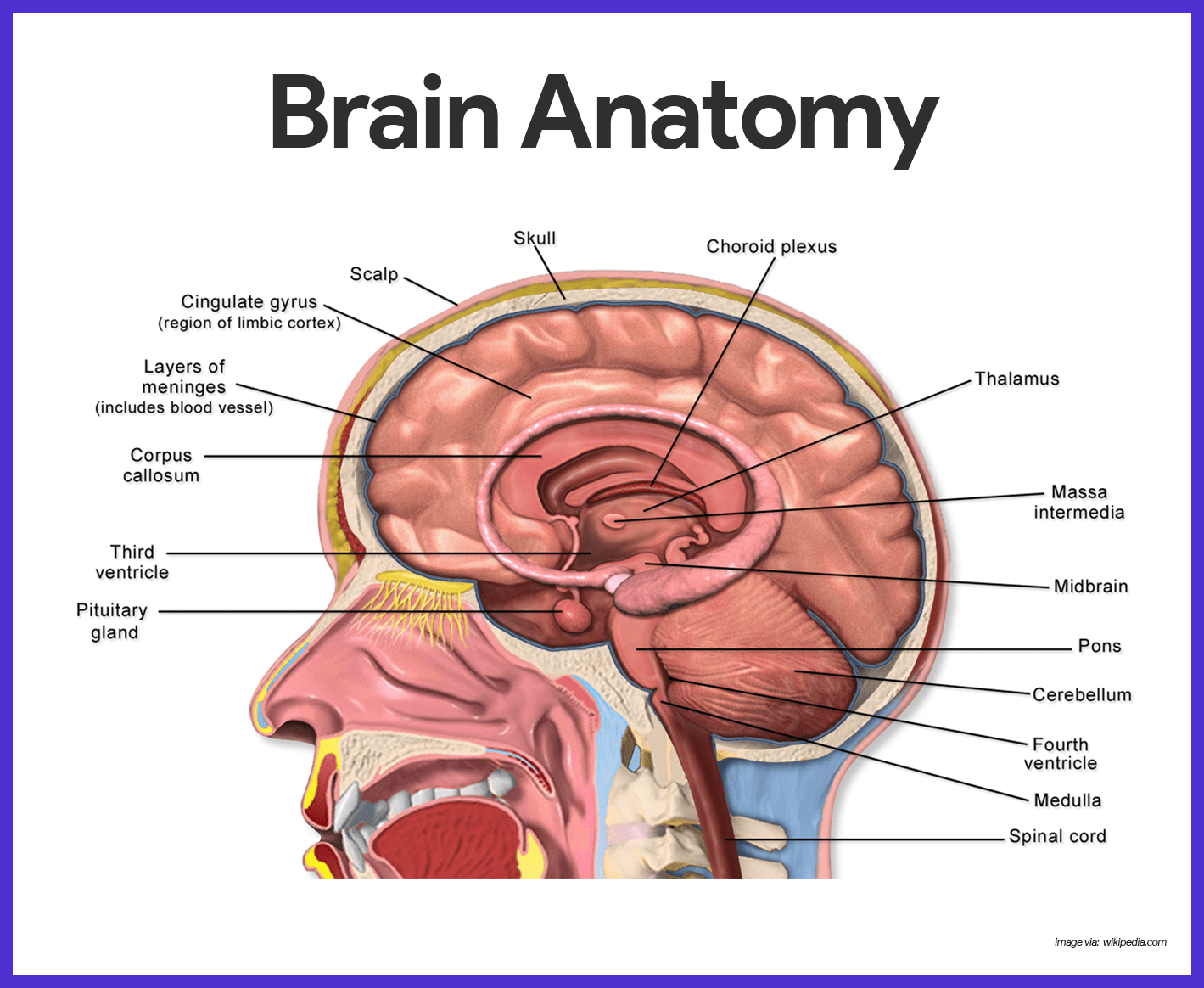
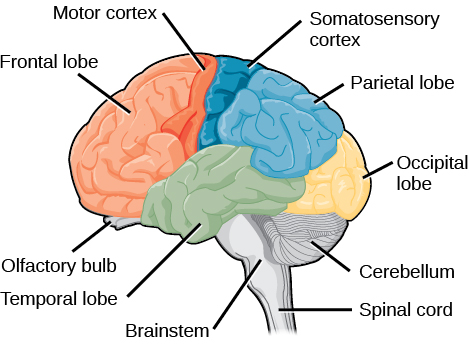
The skull consists of 8 cranial bones and 14 facial bones. The cerebrum, the diencephalon, the brain stem, and the cerebellum. Correct The word fascicle means "bundle" or "cluster." We have seen this term before, when we discussed the structure of muscles.
Start studying Cranial Nerves. Perform and recall one or more functional tests for each cranial nerve pair. Information travels from the receptors in the organ of Corti of the inner ear (cochlear hair cells) to the central nervous system, carried by the vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII).
The name indicates the function or the course. The numbering is based on the order in which the CN emerges from the brain, from ventral to dorsal. Learn about different cranial nerves and their functions by.
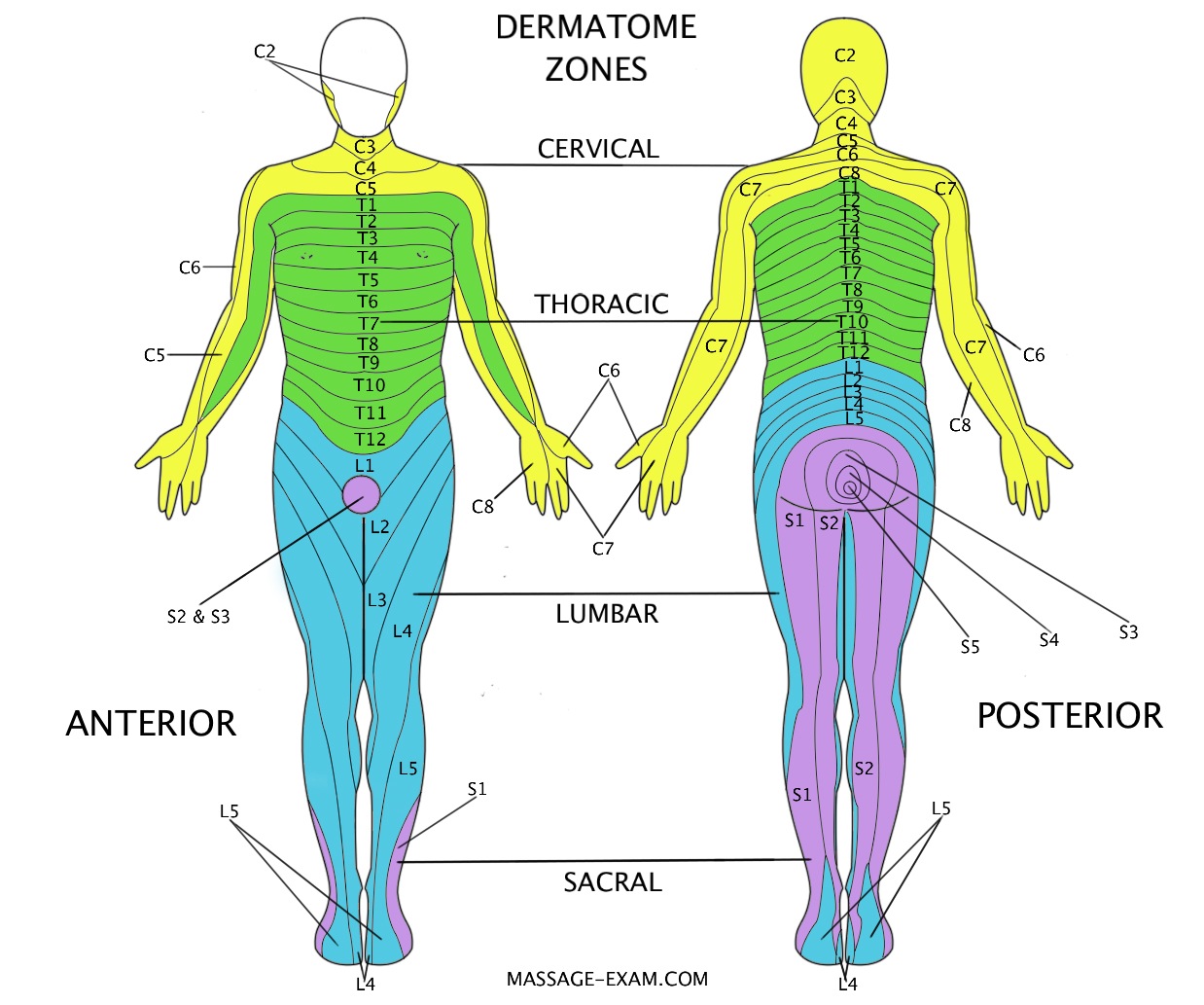
Along the thorax and abdomen, the dermatomes are like a stack of discs, with each section supplied by a different spinal nerve. Game to label the 12 cranial nerves and other visible structures. You’ll be expected to assess a subset of the twelve cranial nerves and identify abnormalities using your clinical skills.
Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools. In humans there are 31 pairs:. Distributed from the head and neck into the thorax and abdomen.
Part A Drag the appropriate labels to their respective targets. Movement of the eye Olfactory Optic Oculomotor Visual acuity Chewing Lateral movement of the eye Trochlear Trigeminal Abducens Smell Pupil constriction Prev 29 of 50Next > rch. This cranial nerve examination OSCE guide provides a clear step-by-step approach to examining the cranial nerves, with an included video demonstration.
Recovery after a stroke depends on many factors, such as the location and amount of brain damage, the person’s age, and the presence of other disorders. The cranial nerves are 12 pairs of nerves that can be seen on the ventral (bottom) surface of the brain. They can arise from a specific part of the brain stem (midbrain, pons or medulla), or from a junction between two parts:.
When stimulated, these nerves increase. There is a printable worksheet available for download here so you can take the quiz with pen and paper. The special senses are served through the cranial nerves, as well as the general senses of the head and neck.
The rest of the cranial nerves contain both afferent and efferent fibres and are therefore referred to as the mixed cranial nerves. Vagus (X) Nerve Mixed cranial nerve. Shrugging the shoulders 2.
Identify each of the examples. Place cranial nerves in order of numeric name beginning with number I. Some of these nerves bring information from the sense organs to the brain;.
Origin of the Cranial Nerves. Focusing the lens of the eye for accommoda-tion;. There are 12 cranial nerves that connect to the brain, including ones that let you smell, see, smile, and swallow.
Match the name of each cranial nerve to its designated number. Drag each cranial nerve function to the name of the cranial nerve it corresponds to. Click on the tags below to find other quizzes on the same subject.
It is derived from the fact that each nerve, one on each side of the pons, has three major branches:. Drag each cranial nerve function to the name of the cranial nerve it corresponds to. The trigeminal nerve is the largest of the cranial nerves.
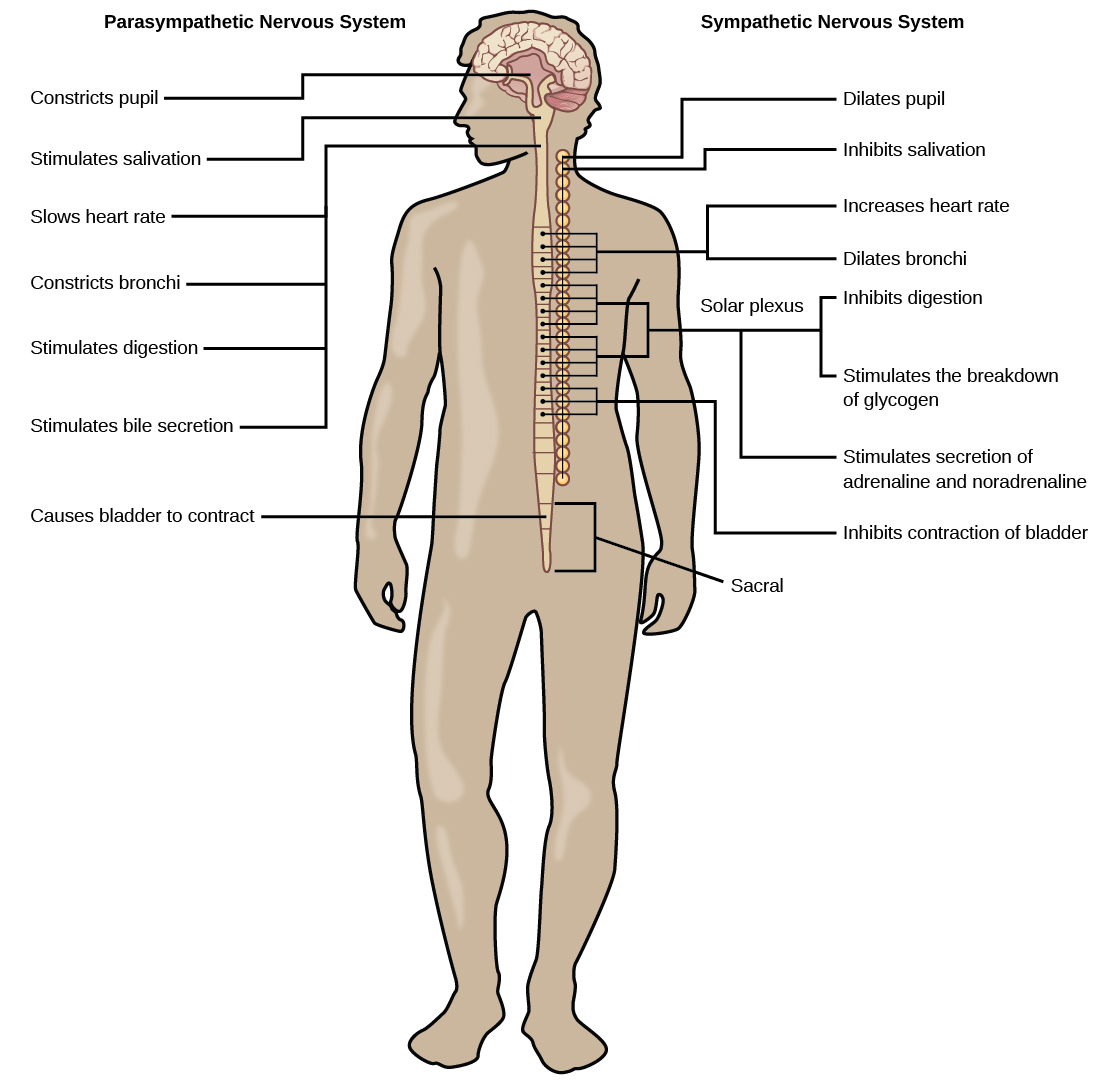
The cranium (skull) is the skeletal structure of the head that supports the face and protects the brain. When stimulated, these nerves prepare the organism for stress by increasing the heart rate, increasing blood flow to the muscles, and decreasing blood flow to the skin. This quiz has tags.
Take the pre-test to get your own personalized study plan. Every cranial nerve (CN) is assigned a Roman numeral as a name. Terms in this set (24) olfactory nerve (I) Name and number the cranial nerve.
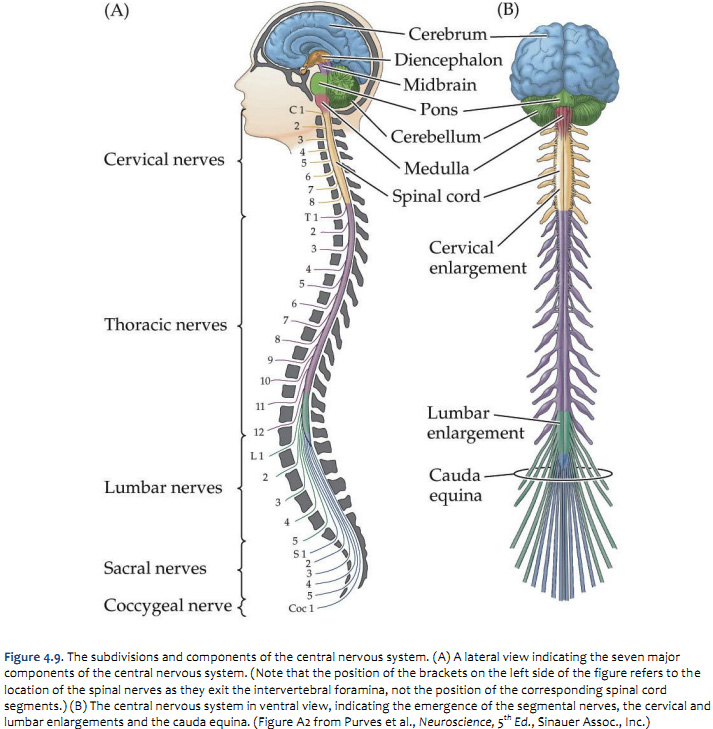
There are eight cervical nerves, twelve thoracic nerves, five lumbar nerves and five sacral nerves. These cells are located in the olfactory epithelium, a mucosal membrane that lines the roof and sides of the nasal cavity. Learn about all 12 of them with our time-saving cranial nerves quizzes and labeling exercises.
The olfactory nerve (CN I) and optic nerve (CN II) originate from the cerebrum. The auditory pathway conveys the special sense of hearing. Sensory neurons deal with a variety of sensations such as proprioception, and stretching.
There are twelve cranial nerves in total. The 12 cranial nerves are the abducent, accessory, facial, glossopharyngeal, hypoglossal, oculomotor, olfactory, optic, trigeminal, trochlear, vagus, and vestibulocochlear nerve. Name the prominent C-shaped band of nerve tracts that connect the right and left cerebral hemispheres to each other.
The brain and the spinal cord are the central nervous system, and they represent the main organs of the nervous system. The twelve cranial nerves are a group of nerves that start in the brain and provide motor and sensory functions to the head and neck. Reconstruct the orthogonal views of the facial nerve (cranial nerve VII) at the level of the CPA, meatus of the IAC, and fundus of the IAC as described under step 4.2.3.
Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools. There are twelve cranial nerves, which are designated CNI through CNXII for “Cranial Nerve,” using Roman numerals for 1 through 12. Show transcribed image text.
Provide the name and number of the cranial nerves involved in each of the following activities, sensations, and disorders. Provide the name and number of the cranial nerves involved in each of the following activities, sensations, or disorders:. This is part of the human anatomy pages about the nervous system.
The spinal cord is a single structure, whereas the adult brain is described in terms of four major regions:. Other cranial nerves are connected to glands or internal organs such as the heart and lungs. It relays sensory data to the brain, and it is responsible for the sense of smell.
Game to label the 12 cranial nerves and other visible structures. Cranial nerves III – XII arise from the brain stem (Figure 1). Spinal nerve, in vertebrates, any one of many paired peripheral nerves that arise from the spinal cord.
Nerves arising from the spinal cord are the spinal nerves.There are 12 pairs of cranial nerves and these pairs of nerves passage through foramina in the skull, either individually or in groups.Cranial nerves are traditionally referred to by Roman numerals and these numerals. Most of them are sensory fibers but some are motor and other are mixed as well. Designed for Harvard Extension School BIOS E-65c.
The midbrain, pons and medulla oblongata comprise the brainstem. Drag each cranial nerve function to the name of the cranial nerve it corresponds to Hearing Facial VestibulocochlearGlossopharyngeal Elevation of the scapulae Motor. In humans, the olfactory epithelium is small.
The olfactory nerve is only one of the 12 cranial nerves. The bones are listed in Table , but note that only six types of cranial bones and eight types of facial bones are listed because some of the bones (as indicated in the table) exist as pairs. Controlling high blood pressure, high cholesterol levels, and high blood sugar levels and not smoking help prevent strokes.
- Vagus - trigeminal - optic - facial - accessory - vestibulocochlear - glossopharyngeal - olfactory - abducens - oculomotor - trochlear - hypoglossal. They can be classified as sensory nerves, motor nerves, or a combination of both, meaning that the axons in these nerves originate out of sensory ganglia external to the cranium or motor nuclei within the brain. Smelling a flower 3.
Provide the name, number, and functions of the twelve pairs of cranial nerves. Cranial Nerves Chart Listed below is a chart of the 12 cranial nerves, the assessment technique used, if the response elicited is normal, and how to document it. This is an online quiz called 12 Cranial Nerves (Function).
Motor IV Trochlear Eye movements, proprioception Motor V Trigeminal Sensations of the head and face, chewing movements, and muscle sense. Cranial Nerves Cranial Nerve Name Function Sensory, Motor, or Both I Olfactory Sense of Smell Sensory II Optic Vision Sensory III Oculomotor Raise eyelids, move eyes, regulate the size of pupils, focus of lenses. Mixed VI Abducens Produce.
Each pair connects the spinal cord with a specific region of the body. This pathway ultimately reaches the primary auditory cortex for conscious perception.In addition, unconscious processing of auditory information occurs in. Its name, trigeminal, means three twins.
Start studying A&P Lab Exercises 17&19. The movement of the eyes, face, tongue, throat, and neck are all under the control of cranial nerves. It is also known as cranial nerve 1 because it is the shortest of the cranial nerves and one of only two nerves (the other is the optic nerve) that bypass the brain stem and connect directly to.
Learn with flashcards, games, and more — for free. There are 12 cranial nerves that are often forgotten by nurses, so with that in mind, here’s a free assessment form that you can use!. Expert Answer 93% (15 ratings) Olfactory help in smell Optic help in visual acuity Oculomotor help in pupil constriction Trochlear help view the full answer.
Nerves can be further categorized as spinal nerves or cranial nerves based on where they connect to the central nervous system. Overview of cranial nerves. Optic nerve (II) Name and number the cranial nerve.
The vagus nerve (cranial nerve X) has autonomic functions in the thoracic and superior abdominal cavities. There are 12 pairs of cranial nerves.These 12 pairs of cranial nerves help us to perform our daily activities in a more accurate way.This possible because they take part of the information of our sens view the full answer. Also known as CN1, the olfactory nerve is the first of 12 cranial nerves located within the head.
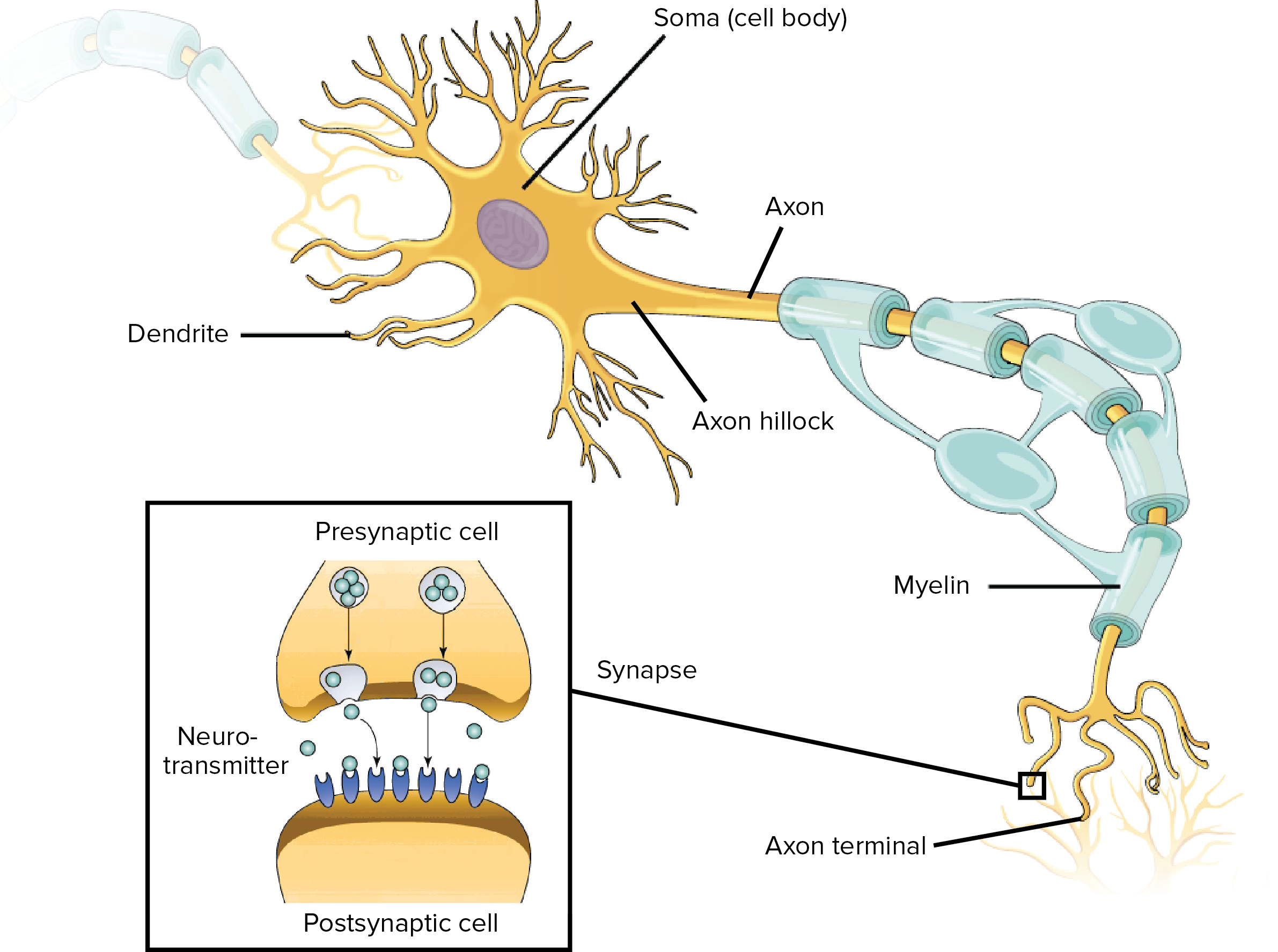
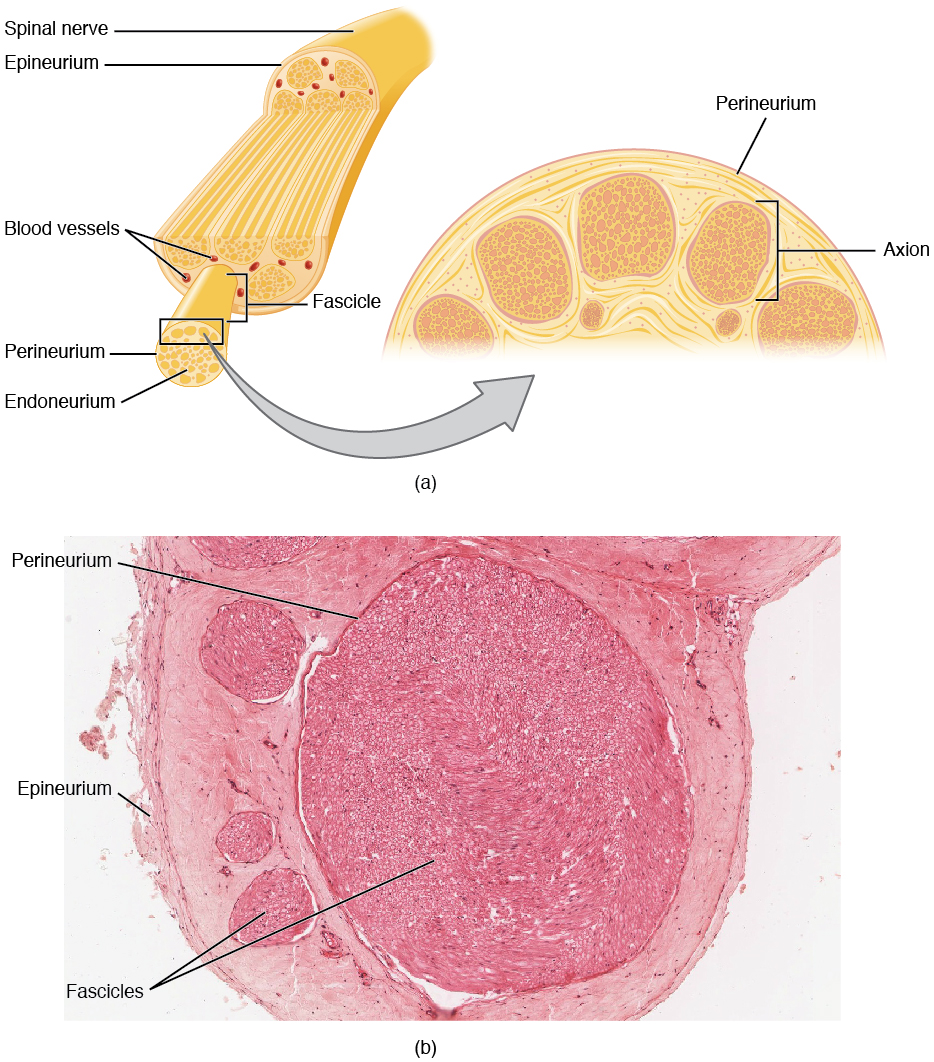
It is subdivided into the facial bones and the brain case, or cranial vault ().The facial bones underlie the facial structures, form the nasal cavity, enclose the eyeballs, and support the teeth of the upper and lower jaws. Chapter 13 Reading Question 2 Part A A bundle of axons within a nerve is called a _____. Each cranial nerve has its unique anatomical characteristics.
Answers from quiz answer key and textbook. Pick an audience - or yourself - and it'll end up in their play queue. 8 cervical, 12 thoracic, 5 lumbar, 5 sacral, and 1 coccygeal.
Cranial nerve examination frequently appears in OSCEs. Place cranial nerves in numerical order, beginning with cranial nerve (CN) I. List of the 12 Cranial Nerves with concise information about the name, number and functions of each.
Each of these nerves relays sensation, including pain, from a particular region of skin to the brain. The nerve fibres of the parasympathetic nervous system are the cranial nerves, primarily the vagus nerve, and the lumbar spinal nerves. Identify major components of the brain.
Connect system lab quiz Saved Drag each cranial nerve function to the name of the cranial nerve it corresponds to. These 12 cranial nerves carry different fiberes. Check for out of plane traversing of the nerve and correct the plane orientation respectively at each level of reconstruction.
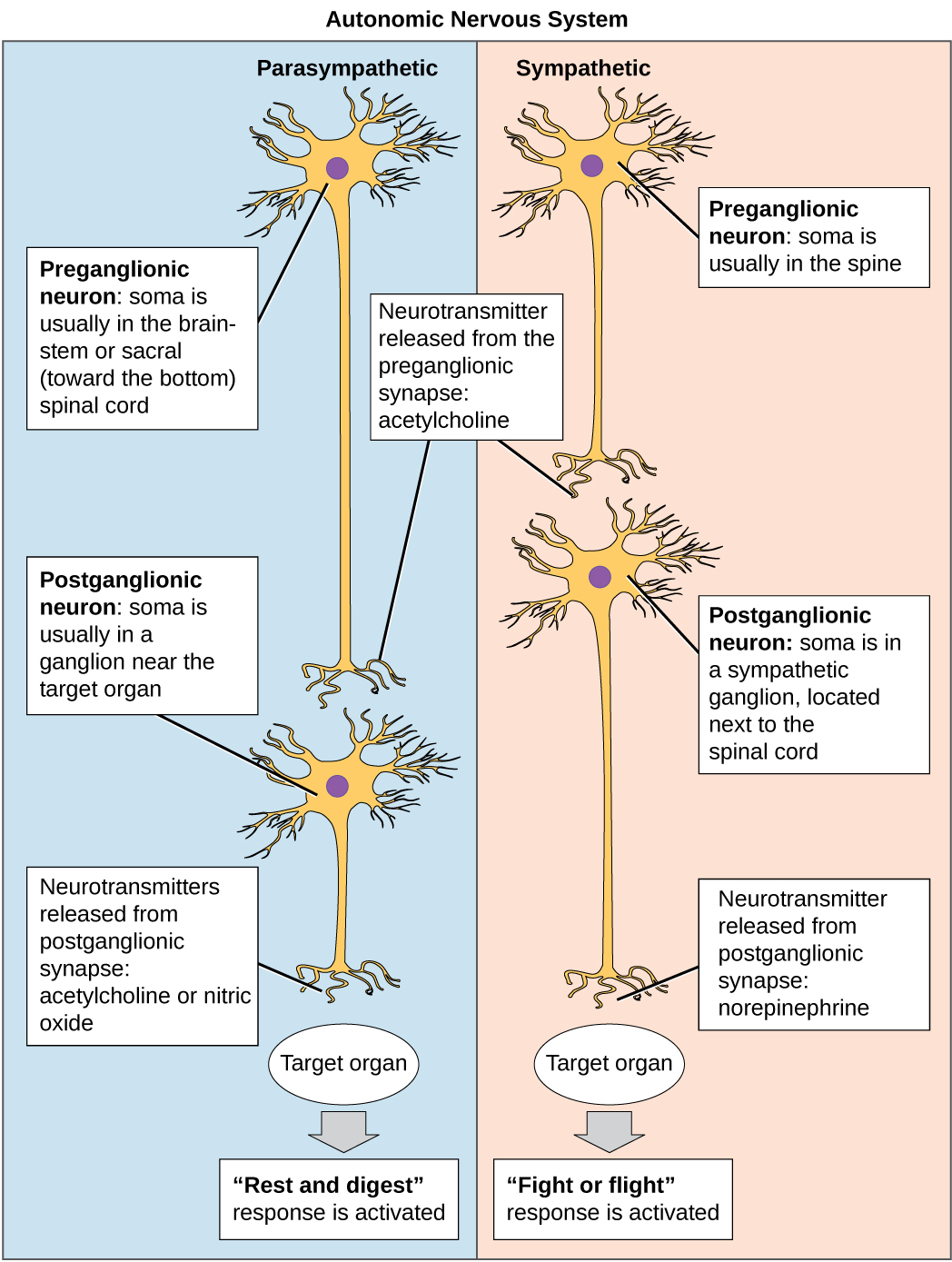
However, the vagus nerve has branches to most of the internal organs and is the part of the autonomic nervous system. The image depicts an example of the autonomic nervous system and an example the somatic motor system. There are 12 of them, each named for their function or structure.
Cranial Nerves and Brain Components Objectives After completing this laboratory, the student will be able to:. Motor neurons arise from the medulla and supply muscles of the pharynx, larynx, and soft palate that are involved in swallowing and vocalization. They enervates different organs in head and neck region (with the exception of vagus nerve).
Cranial Nerves a) abducens nerve (VI) b) accessory nerve (XI) c) cerebellum d) cerebral peduncle. Another 31 pairs of nerve roots (one sensory, one motor) branch out from your.
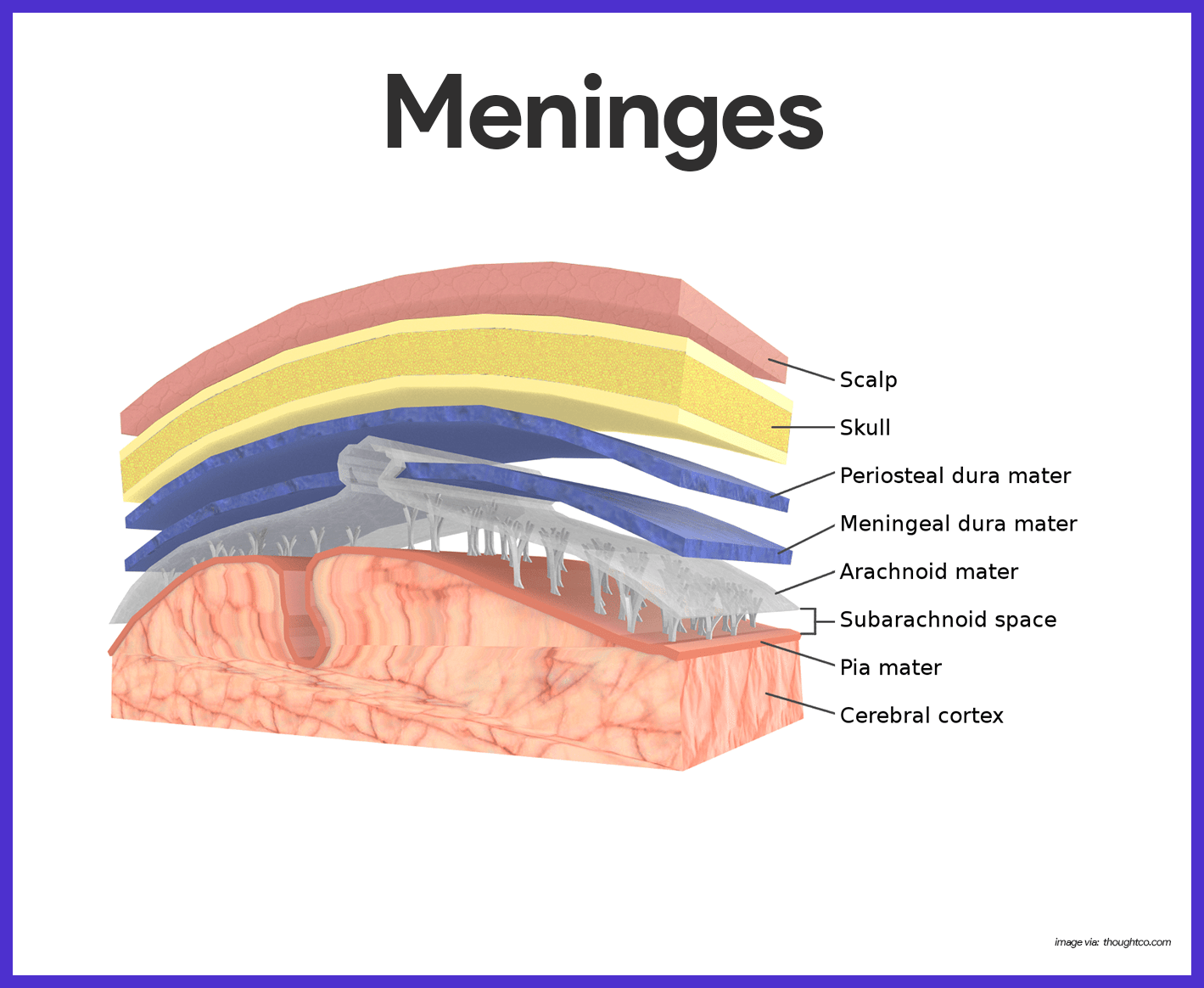
Nervous System Anatomy And Physiology Nurseslabs

A P Lab Test 2 Flashcards Quizlet
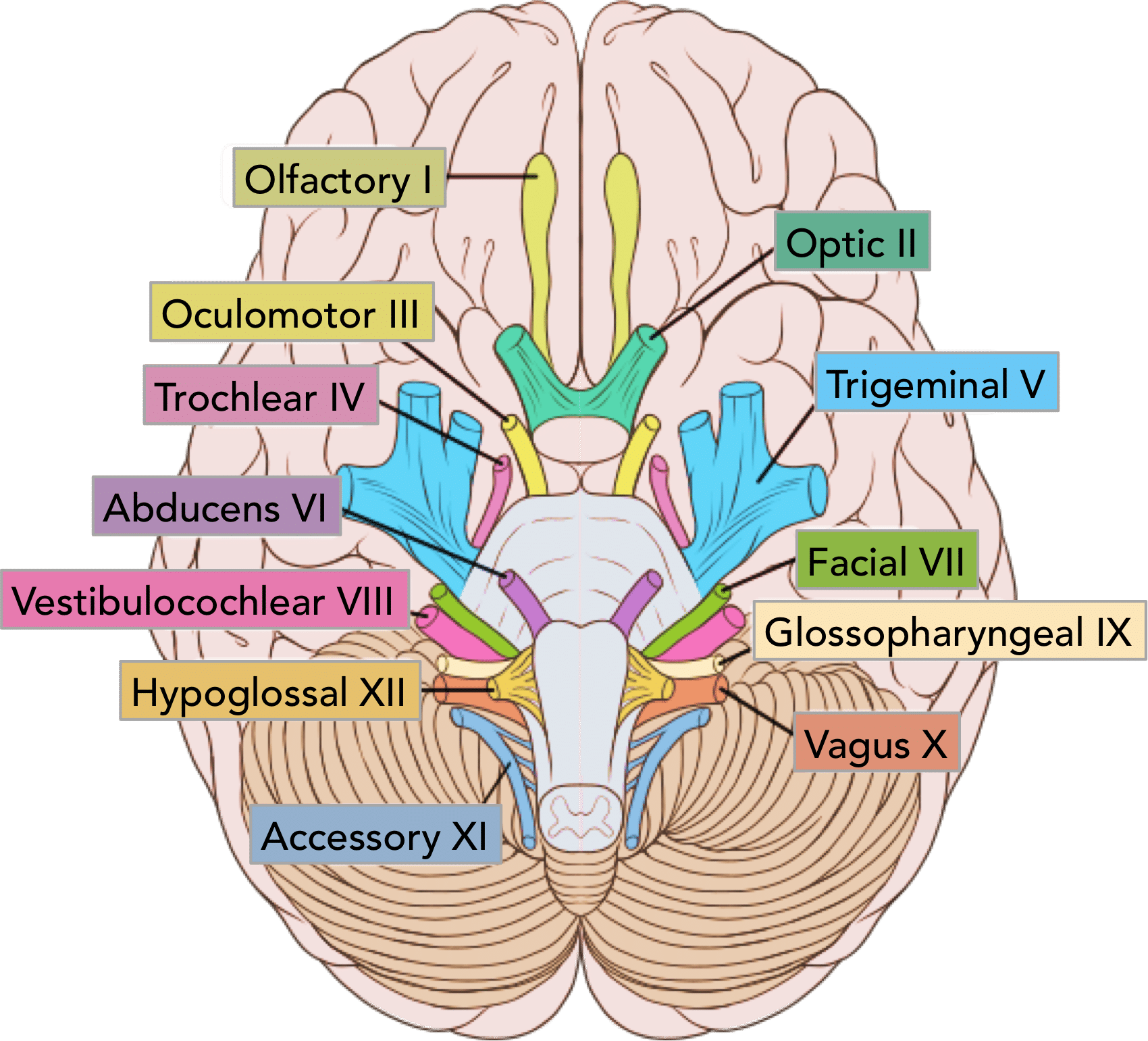
Summary Of The Cranial Nerves Teachmeanatomy
Section Summary Nervous System By Openstax Page 7 48 Jobilize

Chapter 11 Homework Flashcards Quizlet
11 6 Nervous System Concepts Of Biology 1st Canadian Edition
Massage Therapy Terminology Glossary
Overview Of Neuron Structure And Function Article Khan Academy

1 4 The Somatic Nervous System Neuroscience Canadian 1st Edition Open Textbook
1

Off Topic Your Gonads Are Innervated By Your Cranial Nerves Sauropod Vertebra Picture Of The Week
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/11647/worksheet_cranial_nerves_unlabeled.png)
Cranial Nerves Quizzes And Labeling Exercises Kenhub
Nervous System Anatomy And Physiology Nurseslabs

This Week In Mac Sports 9 15 The Mac Weekly

14 5 Sensory And Motor Pathways Anatomy Physiology

11 3 Explain The Criteria Used To Name Skeletal Muscles Anatomy Physiology
Summary Of The Cranial Nerves Teachmeanatomy

Bio 181 Ch 13 14 Pearson Homework Answers Pdf Notonexam Ch13 Due 11 59pmonthursday December21 17 Gradingpolicy Parta Answer P Course Hero
Anatomy Exam 2 Flashcards Easy Notecards

Duke Neurosciences Lab 2 Spinal Cord Brainstem Surface And Sectional Anatomy

14 5 Sensory And Motor Pathways Anatomy Physiology
13 4 The Peripheral Nervous System Anatomy And Physiology

In Vivo Morphometric Analysis Of Human Cranial Nerves Using Magnetic Resonance Imaging In Meniere S Disease Ears And Normal Hearing Ears Protocol
Solved Let S Begin With An Overview Of The Cranial Nerves Chegg Com
2
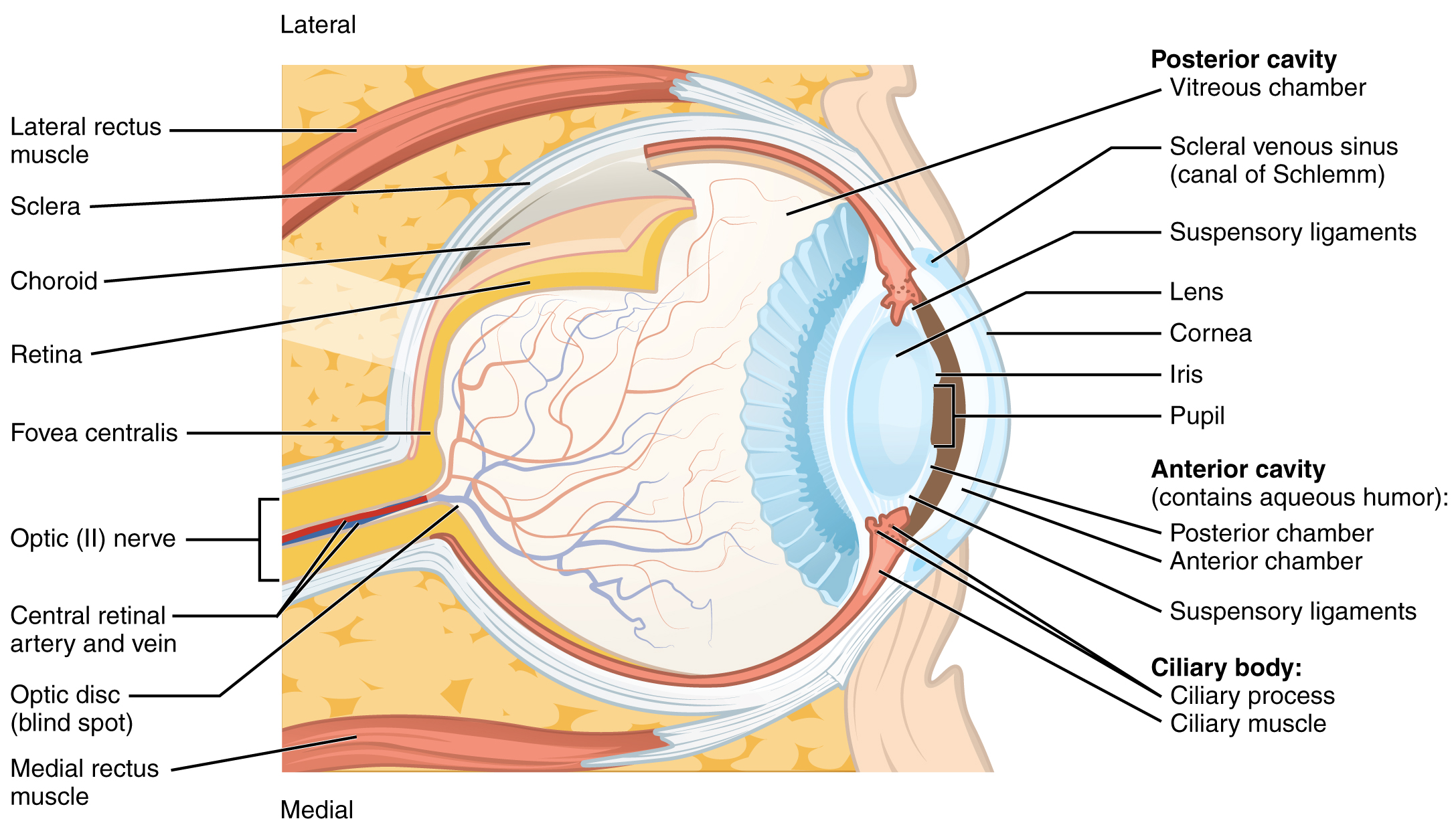
14 1 Sensory Perception Anatomy And Physiology
2

Openstax Anatomy And Physiology Ch14 The Somatic Nervous System Top Hat

Duke Neurosciences Lab 2 Spinal Cord Brainstem Surface And Sectional Anatomy
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/11648/overview_cranial_nerves_diagram.jpg)
Cranial Nerves Quizzes And Labeling Exercises Kenhub

Bio 181 Ch 13 14 Pearson Homework Answers Pdf Notonexam Ch13 Due 11 59pmonthursday December21 17 Gradingpolicy Parta Answer P Course Hero

A P Lab Test 2 Flashcards Quizlet

Openstax Anatomy And Physiology Ch14 The Somatic Nervous System Top Hat
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/13904/YEAulUfDNLIEmjBZ6nhFUQ_Medulla_spinalis_m01.png)
Neural Pathways And Spinal Cord Tracts Anatomy Kenhub
2

10 Google Classroom Human Anatomy Ideas In Google Classroom Anatomy Electron Configuration

Bio 181 Ch 13 14 Pearson Homework Answers Pdf Notonexam Ch13 Due 11 59pmonthursday December21 17 Gradingpolicy Parta Answer P Course Hero
Q Tbn 3aand9gct Unkjm4oh Dpoav57yjmaqd9mcysbc7qfce0xahdag1eschvl Usqp Cau

Nerve Exits Skull Branches Branchial Somatic Cranial Nerves Anatomy And Physiology Nerve

Bio 181 Ch 13 14 Pearson Homework Answers Pdf Notonexam Ch13 Due 11 59pmonthursday December21 17 Gradingpolicy Parta Answer P Course Hero

7 4 The Vertebral Column Anatomy Physiology

Reflexes Neurons In Action Ck 12 Foundation

Chapter 11 Homework Flashcards Quizlet

In Vivo Morphometric Analysis Of Human Cranial Nerves Using Magnetic Resonance Imaging In Meniere S Disease Ears And Normal Hearing Ears Protocol

11 3 Explain The Criteria Used To Name Skeletal Muscles Anatomy Physiology
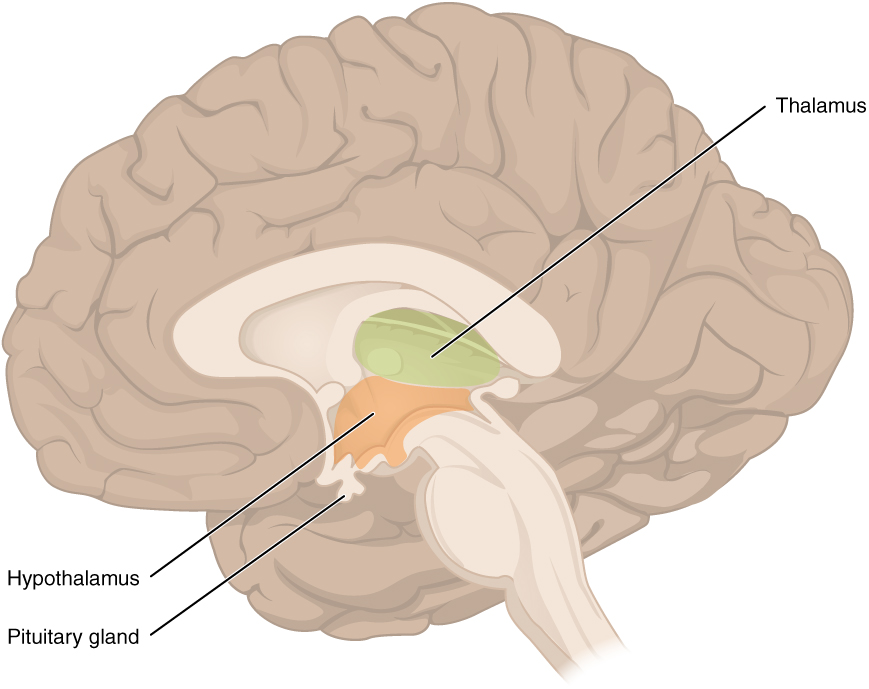
Nervous System Building A Medical Terminology Foundation

Ch 12 Nervous System Exam Mcgraw Flashcards Quizlet

Openstax Anatomy And Physiology Ch14 The Somatic Nervous System Top Hat

Cranial Nerve Testing Introductory Background There Are Twelve

Nursing Tips Cranial Nerves The Harry Potter Way

Chapter 11 Sensory Systems
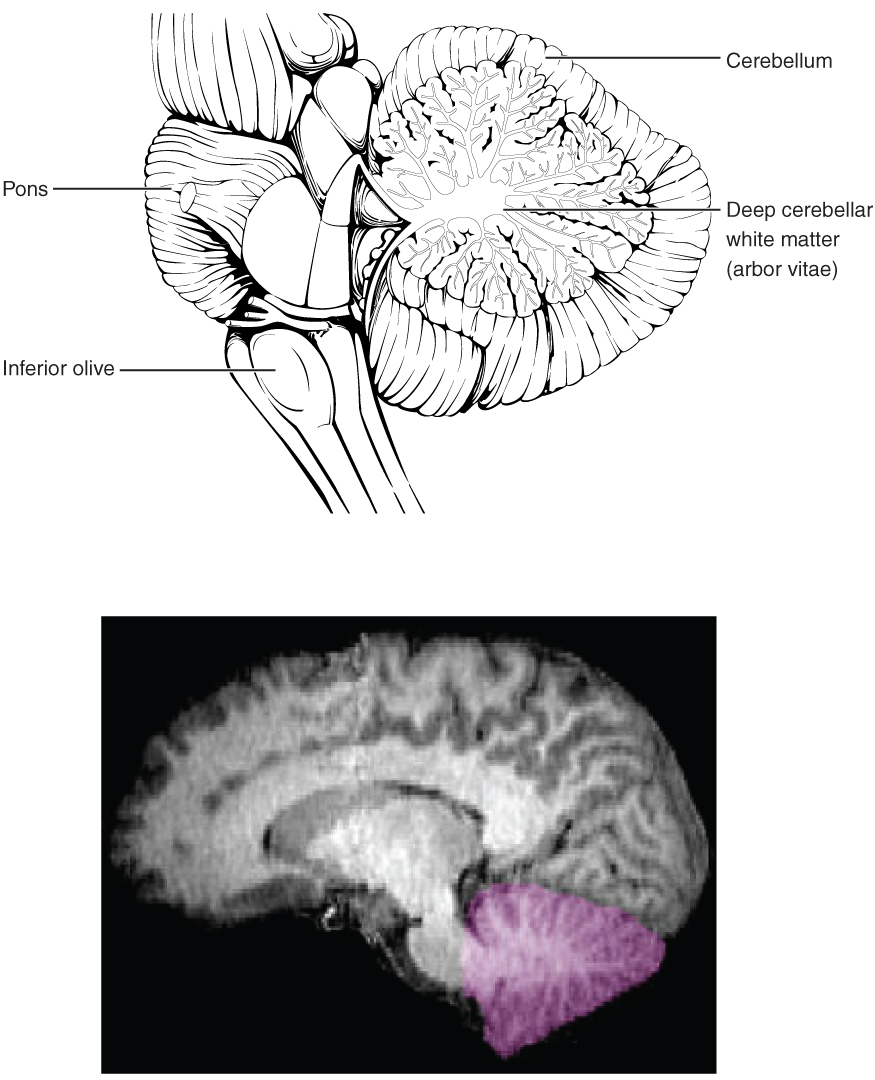
Nervous System Building A Medical Terminology Foundation

Olfactory System Nervous Pathways Of Smell Britannica
2
3

A P Lab Test 2 Flashcards Quizlet

Chapter 11 Sensory Systems
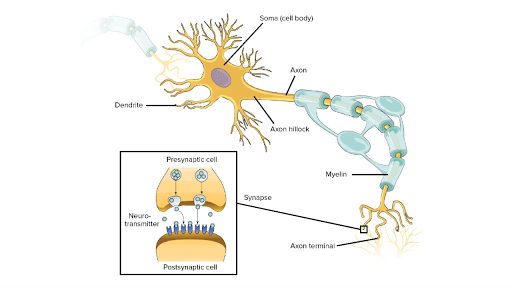
Overview Of Neuron Structure And Function Article Khan Academy

14 3 The Brain And Spinal Cord Anatomy Physiology
Anatomy Exam 2 Flashcards Easy Notecards

Spinal Nerve Definition Function Diagram Number Facts Britannica

In Vivo Morphometric Analysis Of Human Cranial Nerves Using Magnetic Resonance Imaging In Meniere S Disease Ears And Normal Hearing Ears Protocol

Jose S Santiago M D Glasgow Coma Scale Cranial Nerves 12 Pairs Of Nerves That Mostly Serve The Head And Neck Numbered In Order Front To Back Ppt Download
Solved Art Labeling Activity Overview Of Cranial Nerves Chegg Com
Anatomy And Physiology Lab I On Openalg
13 4 The Peripheral Nervous System Anatomy And Physiology

Weakness Brain Spinal Cord And Nerve Disorders Msd Manual Consumer Version
11 6 Nervous System Concepts Of Biology 1st Canadian Edition
Duke Neurosciences Lab 2 Spinal Cord Brainstem Surface And Sectional Anatomy

Chapter 24 Digestive System Flashcards Quizlet

Openstax Anatomy And Physiology Ch14 The Somatic Nervous System Top Hat
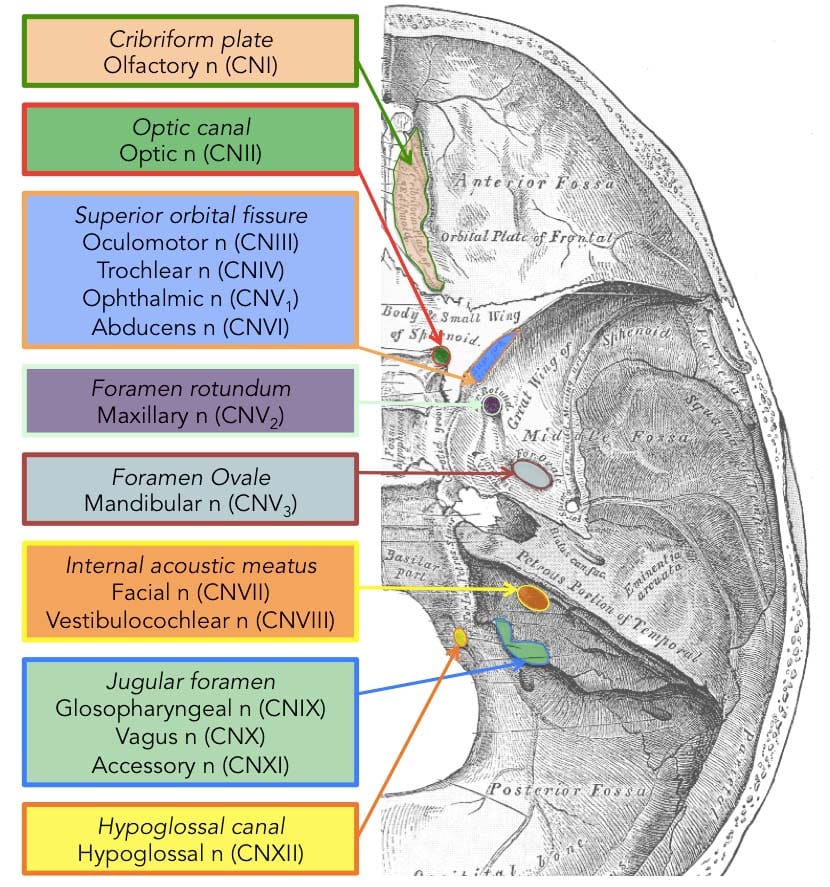
Summary Of The Cranial Nerves Teachmeanatomy
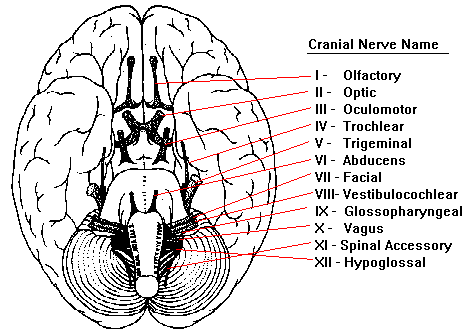
Neuroscience For Kids Cranial Nerves
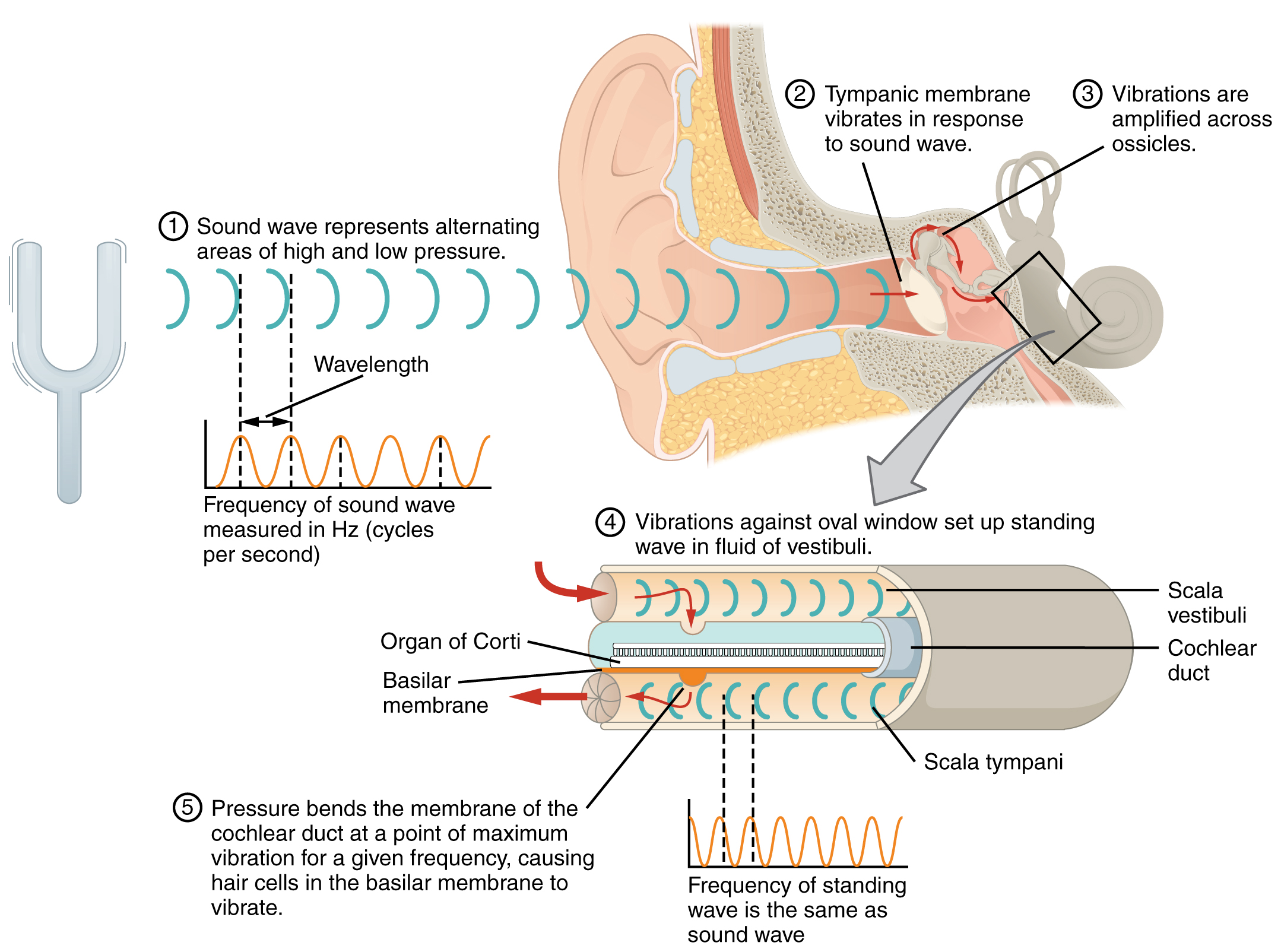
1 4 The Somatic Nervous System Neuroscience Canadian 1st Edition

Surgical Approaches For Brainstem Tumors In Pediatric Patients Abstract Europe Pmc

In Vivo Morphometric Analysis Of Human Cranial Nerves Using Magnetic Resonance Imaging In Meniere S Disease Ears And Normal Hearing Ears Protocol
Anatomy Exam 2 Flashcards Easy Notecards
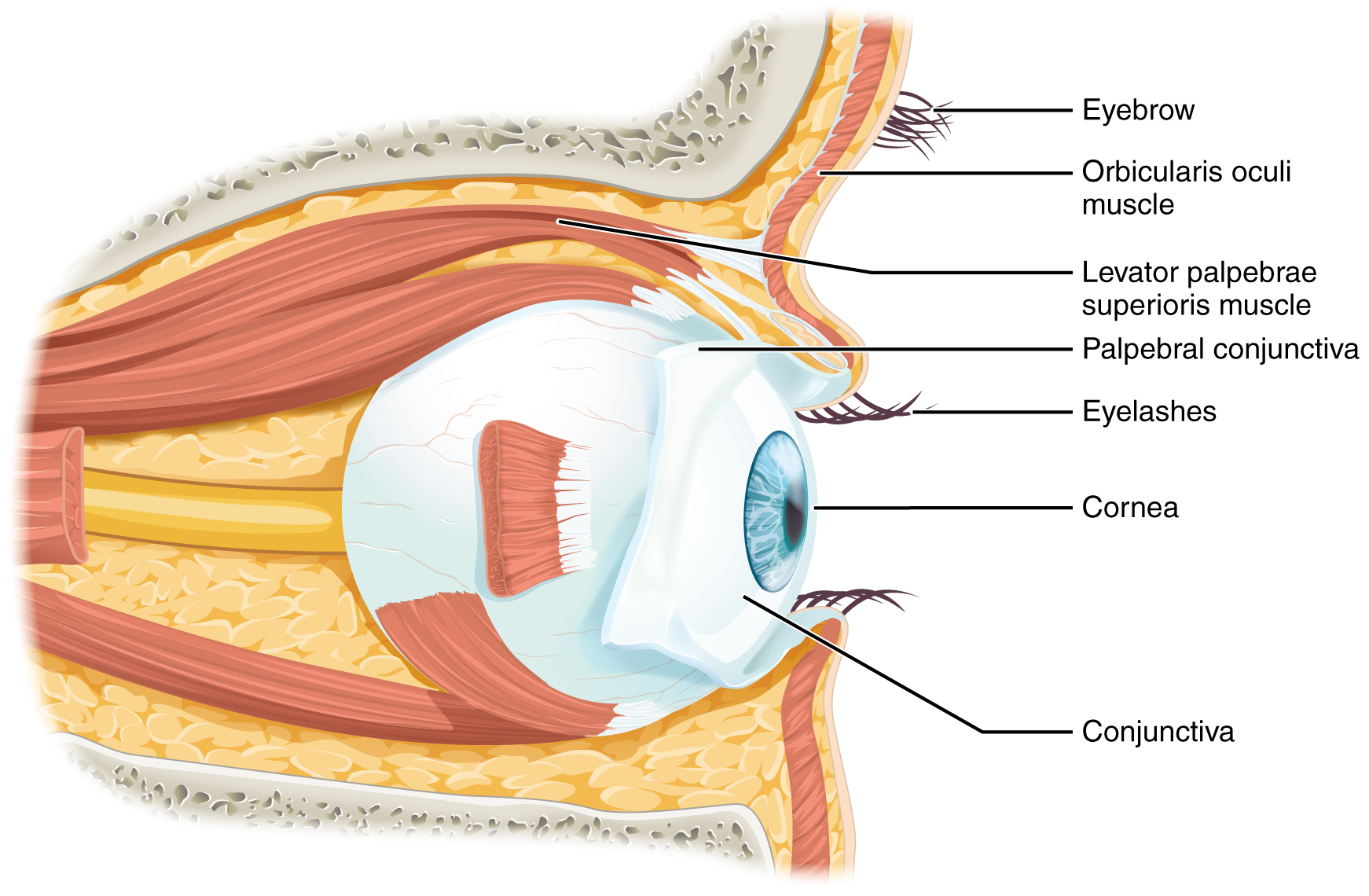
14 1 Sensory Perception Anatomy And Physiology

A P Lab Test 2 Flashcards Quizlet

Openstax Anatomy And Physiology Ch14 The Somatic Nervous System Top Hat

Bio 181 Ch 13 14 Pearson Homework Answers Pdf Notonexam Ch13 Due 11 59pmonthursday December21 17 Gradingpolicy Parta Answer P Course Hero

Openstax Anatomy And Physiology Ch14 The Somatic Nervous System Top Hat

1 4 The Somatic Nervous System Neuroscience Canadian 1st Edition Open Textbook
2
2
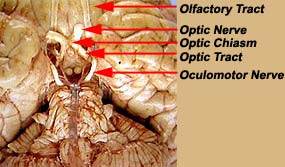
Neuroscience For Kids Cranial Nerves

Spinal Nerve Definition Function Diagram Number Facts Britannica

A P Lab Test 2 Flashcards Quizlet

Overview Of The Cranial Nerves Brain Spinal Cord And Nerve Disorders Merck Manuals Consumer Version
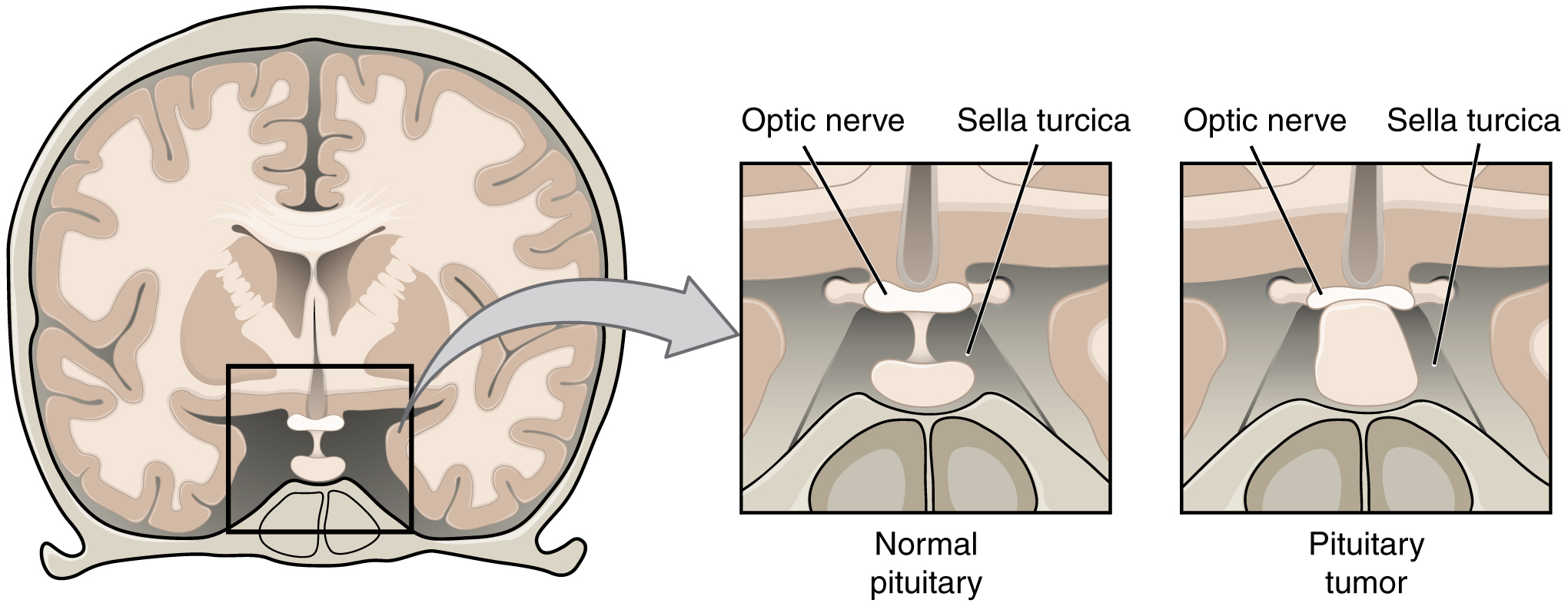
16 3 The Cranial Nerve Exam Anatomy And Physiology
2
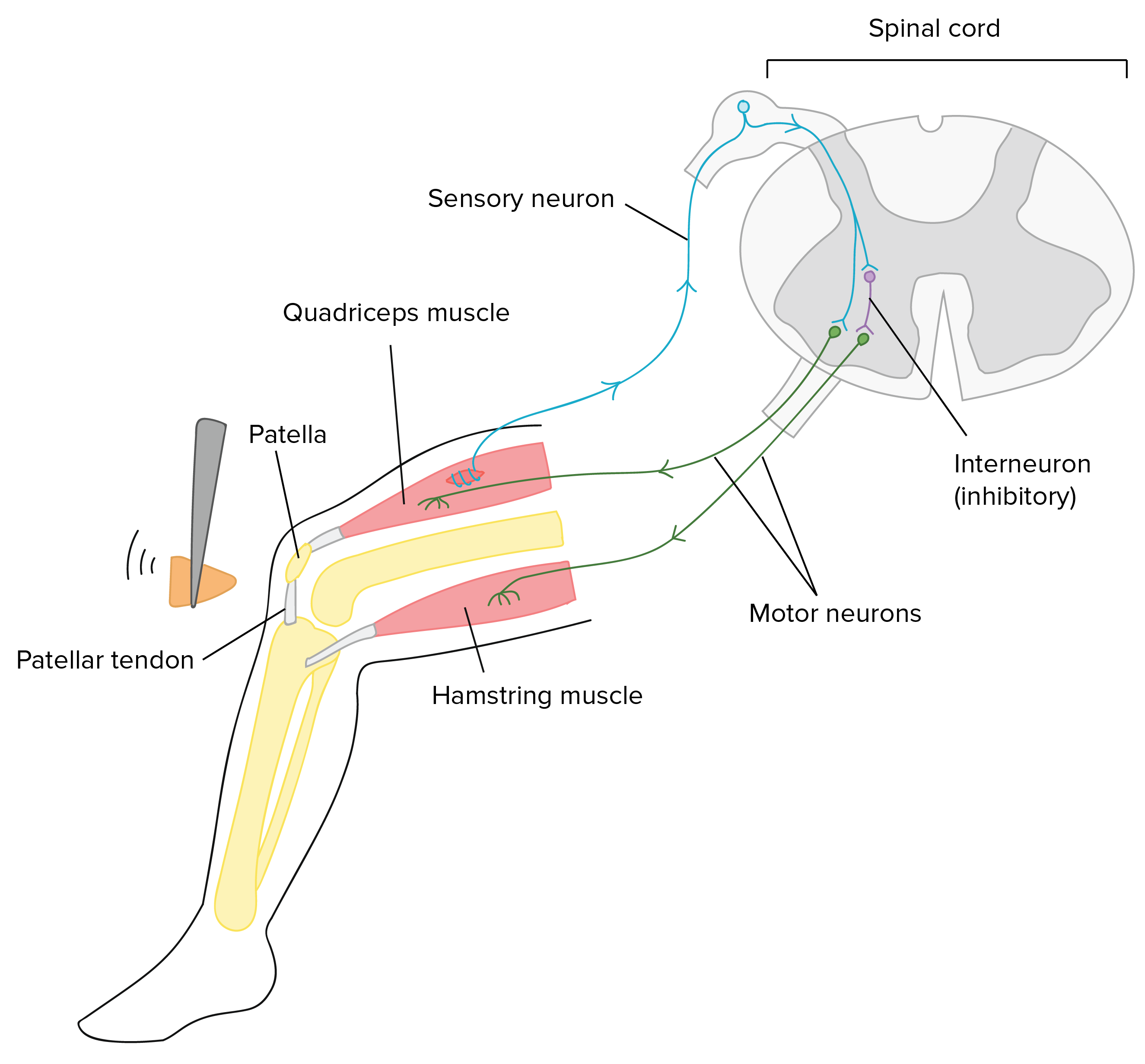
Overview Of Neuron Structure And Function Article Khan Academy

Openstax Anatomy And Physiology Ch14 The Somatic Nervous System Top Hat

1 4 The Somatic Nervous System Neuroscience Canadian 1st Edition Open Textbook
/what-is-the-peripheral-nervous-system-2795465-FINAL-b69e1bb803654212a83d9e68eb4847d0.png)
How The Peripheral Nervous System Works

A P Lab Test 2 Flashcards Quizlet
Anatomy Exam 2 Flashcards Easy Notecards



